We want to share this Cochrane review: Gases for establishing pneumoperitoneum during laparoscopic abdominal surgery.
Objectives: To assess the safety, benefits, and harms of different gases (e.g. carbon dioxide, helium, argon, nitrogen, nitrous oxide, and room air) used for establishing pneumoperitoneum in participants undergoing laparoscopic abdominal or gynaecological pelvic surgery.
Main results: 10 randomized trials with 583 participants were included. In this publication, the authors conducted a comprehensive Cochrane systematic review with meta-analyses. Different gases for establishing pneumoperitoneum were compared to carbon dioxide: nitrous oxide (four trials), helium (five trials), or room air (one trial). All were single‐centre studies and mean age of the participants ranged from 28 years to 49 years.
The rigorous analysis revealed that for:
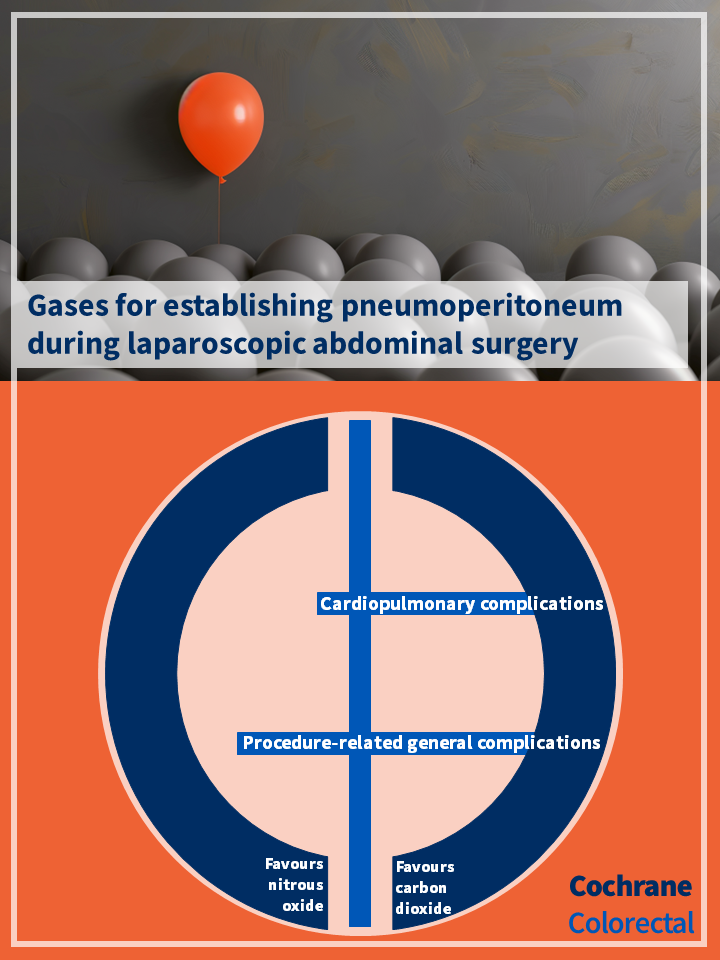
Nitrous oxide versus carbon dioxide:
- The evidence is very uncertain about the effects on cardiopulmonary complications or surgical morbidity. There were no serious adverse events related to either nitrous oxide or carbon dioxide pneumoperitoneum.
Helium versus carbon dioxide:
- The evidence is very uncertain about the effects on cardiopulmonary complications or surgical morbidity. There were three serious adverse events (subcutaneous emphysema) related to helium pneumoperitoneum.
Room air versus carbon dioxide:
- There were no cardiopulmonary complications, serious adverse events, or deaths observed related to either room air or carbon dioxide pneumoperitoneum.
The authors concluded that the evidence is very uncertain about the effects of nitrous oxide, helium, and room air pneumoperitoneum compared to carbon dioxide pneumoperitoneum on any of the primary outcomes, including cardiopulmonary complications, surgical morbidity, and serious adverse events. The safety of nitrous oxide, helium, and room air pneumoperitoneum has yet to be established, especially in people with high anaesthetic risk.
Access publication here: https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD009569.pub4